Introduction
In recent years, themini pchave become popular among tech enthusiasts, gamers, and DIY enthusiasts. With the advanced features they pack into such a small unit, they have become the ultimate level of flexibility, combining high-performance capabilities with a small form factor that tends to appeal to those who value efficiency and customization.
Unlike a regular desktop computer, mini PCs can be moved from place to place with relative ease and are space-saving gadgets that are suitable for those who are tight on space or prefer a streamlined workspace.
For shallow gaming, mini PCs can still compete with larger systems in terms of form factor and mobility. On the other hand, mini PCs are very popular with DIYers looking for specific applications, whether it’s a mini PC for high-end gaming or a workstation, with space optimization being the main factor to consider.
Mini PCs are therefore ready to use, with all sorts of customizations and high-performance components, to meet the needs of those who want cutting-edge technology, but are willing to give up style and convenience.
This guide will introduce you to the different options available while providing some context on how to choose or build a gaming-focused mini PC designed for builders and power users. From pre-built systems to building one yourself, this guide covers all aspects of using a mini PC.
Why Choose a Mini PC for Gaming and DIY?
Mini PCs appeal to most gamers and DIY enthusiasts due to their incredibly advantageous combination of portability, small footprint, and optimal power consumption. Mini PCs have a small footprint, making them particularly suitable for setting up powerful gaming or productivity stations in tight spaces, adding a touch of beauty to small apartments, dorm rooms, or minimalist work environments.
These mobile devices are an ideal choice for users who need to take their setup with them, whether they are dorm warriors or gamers participating in busy LAN parties.
Mini PCs offer nearly as much performance as traditional desktops when installed with high-end components, allowing gamers to enjoy smooth gaming experiences and handle workloads such as other intensive applications without the bulk of a computer.
While laptops offer portability, they can be a compromise when it comes to upgradeability and customization when compared to notebooks. With their smaller size, mini PCs allow DIYers to choose their components, thus tailoring their specific build to meet their performance needs regarding CPU and GPU processing power, as well as cooling systems.
Mini PCs are a great option for people who have limited space, need to travel a lot, or want a convenient build. Their mix of power, portability, and customization gives them every right to be the most versatile and uncompromising choice for anyone who wants a desktop computer.
Key components of a high-performance mini PC
When building or buying a powerful mini PC for gaming and DIY, it is essential to understand the basic hardware components. Each component has a specific role to play in delivering the desired level of fun and smooth multitasking in a compact structure and design.
Central processing unit (processor)
The CPU brings any computer to life, and a powerful CPU is essential for gaming and multitasking. High-performance mini PCs are typically equipped with processorsIntel Core i5OrCore i7or AMD Ryzen processors to deliver top-notch performance for demanding applications. CPU performance makes a big difference in game loading times and the speed of everyday tasks, so the CPU, which balances power and energy efficiency, is very important for mini PCs, especially given space and cooling issues.
GPU (graphics card)
For a gamer, the GPU is one of the most important components for rendering high-quality graphics and delivering a seamless visual experience. Many compact PCs feature an integrated GPU, while others settle for an external GPU, depending on how the gaming performance is used.
Integrated GPUs are suitable for basic applications and light gaming. A good mini gaming PC allows for the installation of a discrete GPU. Selecting compact options allows for the installation of a discrete GPU, such as NVIDIA’s GTX 1650 or RTX 3060. These GPUs deliver performance in small form factors and help deliver the best immersive gaming experience without having to settle for a small space.
LIVING MEMORY
For small gaming PCs, it is recommended to have at least 8GB of RAM, while a higher specification for performance tasks or streaming is 16GB or more. Adequate RAM allows any system to run multiple applications smoothly, ensuring a seamless gaming or productivity experience.
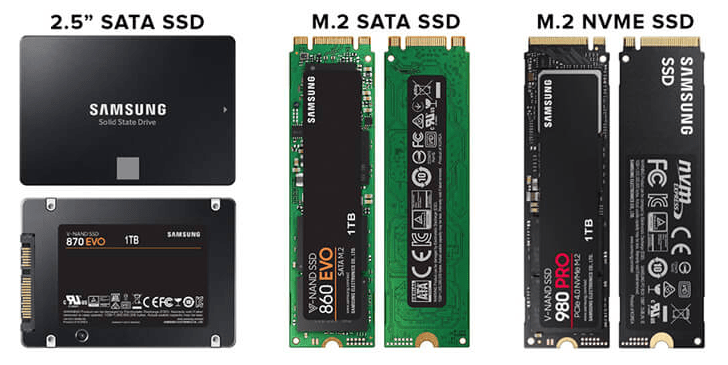
Storage (SSD vs. HDD)
Solid-state drives (SSDs) offer much faster read and write speeds than their traditional counterparts, making them a much more recommended storage option; however, they do impact system load times and responsiveness.
Most mini PCs have the option to install both SSDs and traditional hard drives. This allows the user to choose speed over capacity. A 256GB or 512GB drive should be sufficient for any performance-conscious gamer, while HDD storage is suitable for those who want to store large files and media.
Cooling systems
Effective cooling is essential for high-performance mini computers, as the small size of the device makes it impossible to avoid heat buildup. Therefore, mini PCs use clever cooling solutions, such as liquid cooling systems or high-efficiency fans, to control the temperature.
Cooling allows components to run longer and better, maintaining consistent performance even during intense gaming. It would be best if you choose a mini PC with a good cooling system or build your own mini PC with many cooling devices to avoid overheating and slow performance.
The Best Mini PCs for Gaming in 2024
When it comes to powerful compact gaming PCs in 2024, there are several options that stand out for their power, compact design, and advanced capabilities. Here’s a closer look at three of the top contenders:
GEEKOM XT13 Pro Mini PC
THEGEEKOM XT13 Prois a powerhouse in a tiny form factor that packs some of the latest 13th Gen Intel Core i9-13900H or Core i7-13620H processors, along with impressive Intel® Iris® Xe integrated graphics. While it’s not designed as a lightweight gaming solution, you can still enjoy some of the most popular games on the market, especially when it’s equipped with up to 64GB of dual-channel DDR4 memory, which helps eliminate bottlenecks in loading times and multitasking for both gaming and productivity tasks.
Brilliant Ports and Excellent Cooling: This small PC is equipped with two USB4 ports for cutting-edge connectivity, as well as two HDMI 2.0 ports that give you plenty of high-resolution outputs for multiple displays, perfect for creating a multi-monitor gaming space. The computer’s small size doesn’t mean it’s a thermal powerhouse, as the latest cooling system keeps your PC cool, even when you’re gaming hard and streaming for a long time.
GEEKOM Mini PC GEEKOM A7
If you prefer AMD,the GEEKOM A7 mini PC can boast impressive enough specs to house an 8-core AMD Ryzen 9 7940HS to give you desktop-grade performance suitable for AAA titles. It packs an AMD Radeon 780M graphics card, making it a great option for gamers looking for good visuals and smooth gameplay. The A7’s Ryzen 7 7840HS can reach a frequency of 5.1 GHz, while the Ryzen 9 7940HS tops out at 5.2 GHz, allowing it to tackle all types of applications.
It also supports 32GB of RAM, in case the charm of a workstation strikes. Internal storage, combined with an SSD hard drive, can reach 2TB, which is ideal for a large number of game files and very fast loading times. With its 7nm architecture and 45W TDP, the A7 has found the balance between performance and energy efficiency, making it a gaming-oriented PC that should suit any gamer who needs a compact PC.
GEEKOM MEGAMINI G1
In the small gaming machine market,GEEKOM MEGAMINI G1 offers a processorIntel Core i9-13900H coupled with a dedicated Nvidia GeForce RTX 4060 GPU with 8GB VRAM. It is currently the world’s smallest water-cooled PC, this combination delivers high-quality gaming experiences for smooth performance to play graphically intensive games and VR applications. The MEGAMINI G1 features 32GB DDR5 RAM and up to 2TB SSD storage, with high speed and capacity, which is perfect for gamers with large libraries and multitasking needs.
In terms of connectivity, the MEGAMINI G1 is brimming with options: on the front, it has a USB 3.2 Gen 2 Type-A port, a USB 3.2 Gen 1 Type-A port, a 3.5mm audio jack, and an SD card slot. The back panel features a Thunderbolt 4 port, a USB-C port, two HDMI 2.0 outputs, a 2.5G Ethernet port, and a few others. The latter offers considerable flexibility for peripherals and displays. Plus, with Wi-Fi 6E and Bluetooth 5.2, the MEGAMINI G1 offers ultra-fast and stable wireless networking.
These three mini gaming laptops feature some of the world’s best high-performance technologies and a range of options to suit different preferences, from integrated to dedicated graphics cards and configurationsAMDto the configurationsIntel, ensuring there is a little something for every type of player.
DIY Mini PC: How to Build Your Own High-Performance Mini PC for Gaming
Building a top-tier mini PC for gaming is an interesting endeavor for tech enthusiasts, as it is possible to juggle an impressive setup to meet everyone’s absolute needs and goals. With the right components and proper planning, it is possible to assemble a high-end mini PC that offers excellent gaming performance in a tiny package. This will be more of a simple step-by-step guide to help you navigate the direction you need to go.
Choosing the right components
To start building a small, powerful PC, you need to make sure your components are compatible and fit into a small case. The essential components are the CPU, GPU, RAM, storage, motherboard, and cooling system. Look for a CPU that’s optimized for power and efficiency, such as Intel’s Core i5/i7 or AMD’s Ryzen 5/7, both of which are great choices for gaming. For the GPU, choose compact but powerful models like NVIDIA’s GTX 1650 or RTX 3060, which offer great gaming performance without taking up a lot of space.
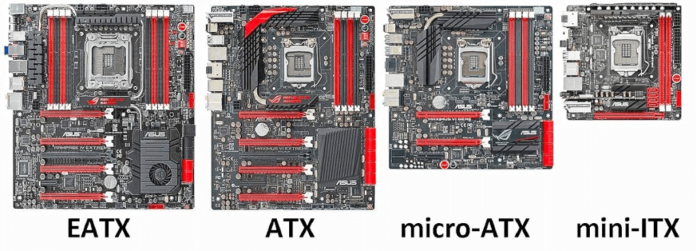
When choosing RAM, try to allocate a minimum space of 16 GB, as it offers more capacity for multitasking without causing lag during games. For storage, it is better to opt for an SSD, which offers the best performance, although the preferred storage space is 512 GB. It is possible to use a hard drive for secondary storage. Care should be taken to choose a motherboard that is compatible with the processor already chosen and that fits into a powerful PC case, as the latter uses the Mini-ITX form factor. It is also imperative to pay attention to the cooling system, as small cases retain heat very easily.
Assembling the Mini PC
After you’ve gathered your components, you move on to assembly. The first step in assembling your system is to mount the CPU onto the motherboard, making sure to line up the pins. Next, install the RAM and storage. Next, mount the motherboard inside the case and secure it; mount the GPU, which may need an adapter or riser cable, depending on your PC configuration. Next, carefully route and connect all cables, including the power supply, which should be compact and efficient (like an SFX PSU) to fit inside the mini PC case.
The second most important thing in high-performance small PCs is cable management for proper circuit flow, which means arranging the cables in a fairly orderly manner. Due to the compactness of these cases, space is a determining factor; cable management reduces the risk of overheating and therefore increases performance.
Testing and adjusting for optimal performance
Once the hardware assembly is complete, it is necessary to check the proper operation of the system. Start the computer and check if the system recognizes the hardware components. Install your operating system. Install essential drivers and programs. Use benchmarking tools such as CPU-Z, GPU-Z or HWMonitor to monitor performance and temperatures. These tools will also help you identify potential bottlenecks and ensure stable operation.
Finally, tune your settings to get the performance you want. This could be adjusting fan speeds, tweaking BIOS settings, or if your components can handle overclocking. Monitor temperatures during CPU-intensive operations, as mini PCs often suffer from packing a lot of power into a compact space and, as a result, have a propensity to run hot. With the right selection and a little planning, your DIY mini PC can play high-performance games while remaining small and efficient and ready for the cramped space of any aspiring gaming enthusiast.
Tips for Optimizing and Maintaining Your Mini PC for Gaming
To keep your high-performance mini PC running smoothly for gaming, it’s essential to optimize and maintain it regularly. Here are some practical tips to keep your mini PC running at its best.
Cooling and airflow management
The compact design of mini PCs makes good thermal management critical, as it affects performance through throttling. Make sure your mini PC is placed in a well-ventilated area, with no obstructions near the air intake and exhaust vents.
Vents and fans should be cleaned regularly to remove dust buildup, which can restrict airflow and increase internal temperatures. If your mini PC allows, incorporate alternative cooling solutions such as compact liquid cooling or high-efficiency cooling fans for small form factor computers.
Software optimization
It is important to keep software up to date to improve performance and security. Regularly update the operating system, drivers, and GPU drivers, as several manufacturers release optimizations to improve gaming performance.
Use utilities such as Windows Game Mode or similar utilities in other operating systems to dedicate more resources to gaming applications. For efficient gaming, it is essential to disable unnecessary startup programs, which frees up system resources, and close background applications.
Storage and Memory Management
You’ll want to organize your game input and output storage for the best gaming setup. For games and other demanding applications, it’s best to use an SSD to get the best performance in terms of load times.
If your mini PC has dual storage, consider using an SSD as your primary drive and then an HDD for additional storage needs. Keep an eye on RAM usage, as insufficient RAM can seriously impact performance during high-load tasks. Adding more memory can also improve multitasking and gaming performance, especially for more demanding titles.
Regular system checks and updates
Run diagnostics on your mini PC regularly to check that all hardware components are working. Use hardware temperature monitoring software such as HWMonitor or MSI Afterburner to monitor CPU and GPU temperatures, especially while gaming. These programs can help you spot potential issues early and take action before they affect performance.
If you take these parameters into account, you can expect your mini PCs to last longer and perform better when needed, enabling smooth gaming experiences at the required pace throughout the lifespan of a mini PC.
Conclusion
Powerful, portable, and customizable mini PCs are a popular choice for the average person and are extremely popular among gamers and DIY enthusiasts. They are ideal as small desktop systems, whether ready-made or custom-built; these systems with miniature architectures do not take up space due to their small size, but can allow you to play on a full desktop computer at your bedside.
If equipped with the right components, maintained, and optimized, mini laptops will allow you to game all night long. Mini PCs offer immense possibilities for customization and enhancement of your entire gaming and tech setup while remaining very compact.