Contents
The motherboard, one of the most important components of a computer, is the circuit board that provides communication between the computer’s central processing unit (CPU), memory, expansion cards and other components. In this article, we will take a closer look at what a motherboard is and its critical role in the functioning of the computer.
What is a motherboard?
The motherboard is the circuit board that brings together the basic components of the computer and ensures communication between these components. It allows other components (processor, memory, storage devices, expansion cards, etc.) to be connected to the motherboard. The motherboard manages data transfer between these components and runs all parts of the computer in harmony.
What Does a Motherboard Do? Functions of the Motherboard
- Component Interconnect: Brings together and physically connects the motherboard, processor, memory, storage devices, expansion cards, and other hardware components.
- Power Distribution: The motherboard provides power management by distributing the electricity from the power supply to all components.
- Data Transmission: Coordinates the operation of the computer by transmitting data between the processor, memory, storage devices, and other components.
Importance of Motherboard:
The motherboard is a critical component that directly affects the performance of the computer. A quality motherboard optimizes communication between components, increases system stability and improves overall performance. Plus, you can customize your PC the way you want, thanks to convenient expansion slots and ports.
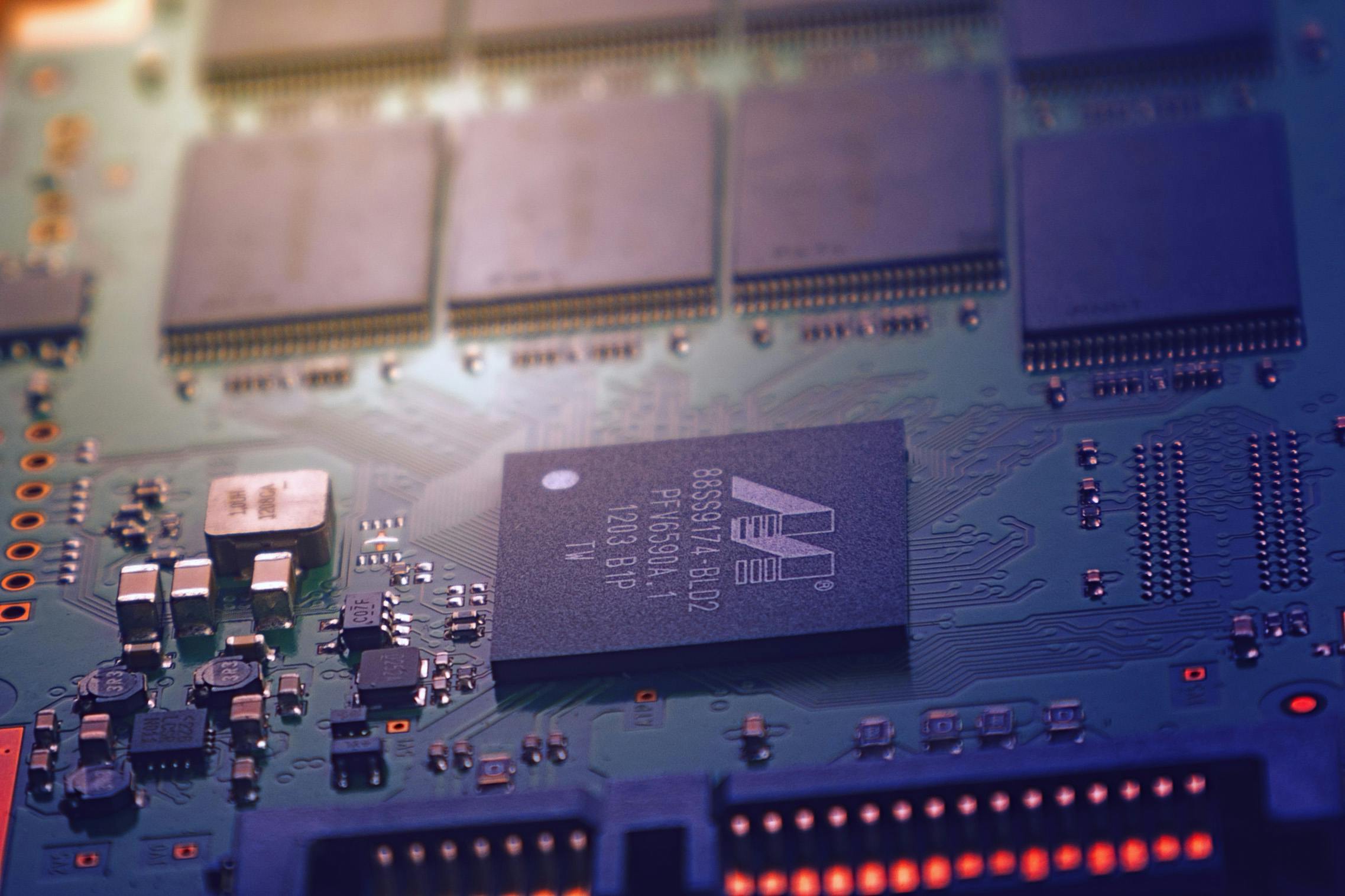
Where is the motherboard located?
The motherboard is located inside a computer’s case. On the inside of the case, you can usually see the motherboard when you remove the right or left side panel of the computer. The motherboard is usually located at the bottom of the case, above or next to the processor cooler. Other components inside the case communicate with each other by connecting directly to the motherboard. For example, the processor is installed in a special slot on the motherboard, memory modules (RAM) are placed in memory slots, and expansion cards are installed in expansion slots. In this way, the motherboard provides data communication between other hardware components and ensures the proper functioning of the computer.
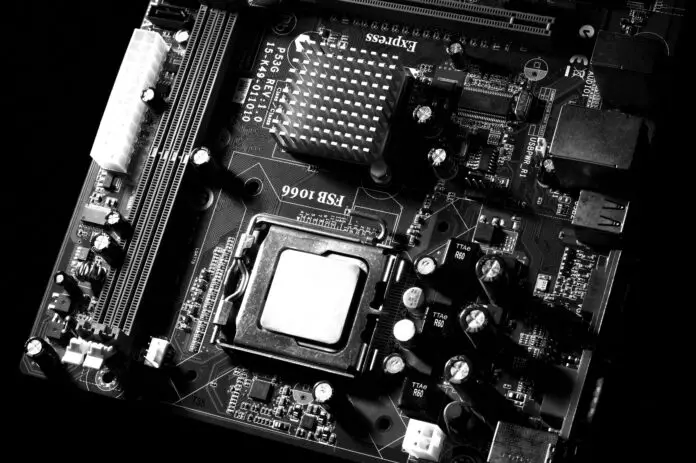
What are the Parts/Components of the Motherboard?
The motherboard is a critical part that brings together the basic components of a computer and ensures communication between these components. Here are the main components of the motherboard:
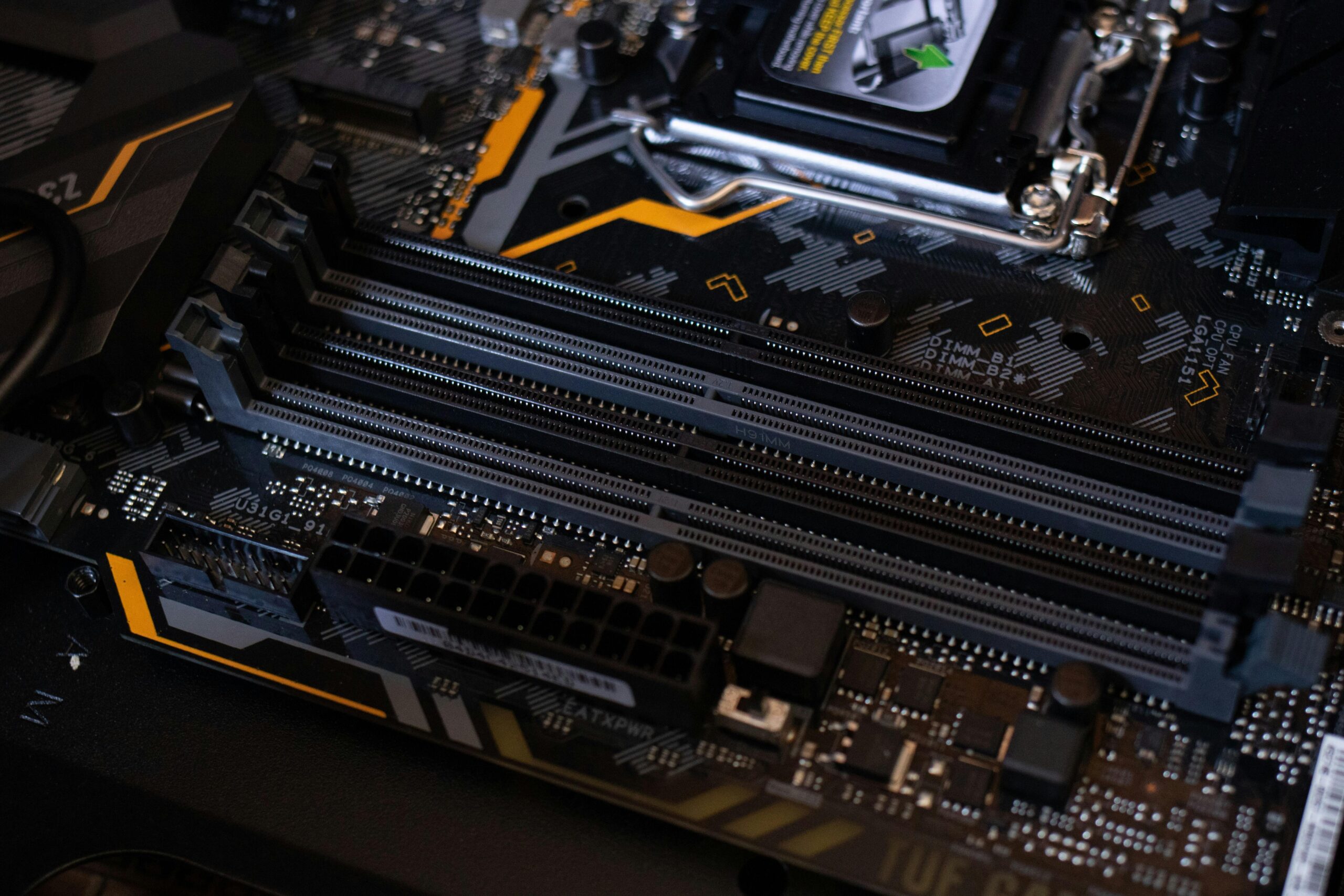
- Processor Socket (CPU Socket): The processor socket is a socket that houses the computer’s processor (CPU) and is installed on the motherboard. There are different motherboard models for different processor types and sockets.
- Memory Slots (RAM Slots): Memory slots are the points where system memory (RAM) is connected to the motherboard. Memory slots can generally be dual-channel or quad-channel and memory modules are installed there.
- Expansion Slots (PCIe, PCIe M.2, etc.): Expansion slots are used to connect additional graphics cards, sound cards, network cards, and other expansion cards to the motherboard. PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) expansion slots are often found on modern motherboards.
- SATA Ports: SATA ports are used to connect storage devices such as hard disk drives, SSDs, and optical drives to the motherboard. These ports are usually located on the edge or side of the motherboard.
- Power Ports: Power ports are the points where the power supply connects to the motherboard. These points are used to meet the power requirements of the motherboard and are usually located at the edge or corners of the motherboard.
- BIOS (Basic Input/Output System): BIOS is the basic system software on the motherboard. It manages the computer’s startup operations and provides basic configuration of the hardware.
- Cooling Elements: Cooling elements on the motherboard are used to prevent the motherboard and the components on it from overheating. These elements can generally be in the form of cooling blocks, heat sinks and fans.
The motherboard is a critical part that brings together the basic components of a computer and determines system performance. Components such as the processor socket, memory slots, expansion slots, storage ports, power ports, and BIOS form the basic building blocks of the motherboard. The combination of these components ensures smooth operation of the computer and delivers optimized performance.
Motherboard Types: The Key to Customizing Your PC
ATX Motherboards:
- ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) motherboards are a wide range of motherboard form factors designed to fit standard desktop computer cases. They have a large surface area and usually offer many expansion slots. Therefore, they are a popular choice for gaming PCs and performance-oriented systems.
Micro ATX Motherboards:
- Micro ATX motherboards have a smaller form factor than ATX motherboards. Therefore, they are ideal for smaller-sized computer cases or compact systems. Micro ATX motherboards generally offer fewer expansion slots but are generally more affordable.
Mini ITX Motherboards:
- Mini ITX motherboards are the motherboards with the smallest form factor. Their smaller size makes them preferred for ultra-compact systems or special usage scenarios such as HTPC (Home Theater PCs). However, they generally have fewer expansion slots and ports.
Gaming-Focused Motherboards:
- Gaming-focused motherboards are generally designed to be compatible with high-performance components and developed specifically to enhance the gaming experience. These motherboards generally have more advanced cooling features, audio and networking technologies, and more expansion slots.
Workstation Motherboards:
- Workstation motherboards are motherboards that are optimized for professional use and have high processor and memory capacity. These motherboards are suitable for applications such as CAD (Computer Aided Design), video editing or data analysis that have powerful hardware requirements to handle intensive workloads.
Things to Consider When Choosing a Motherboard: Customize Your Computer Correctly
Socket Compatibility:
- Your motherboard’s processor socket must be compatible with the processor you choose. For example, there are specific socket types, such as the LGA 1200 socket for Intel processors or the AM4 socket for AMD processors. Compatibility of the processor and motherboard ensures stable operation of your computer.
Memory Support:
- The memory type and speed supported by your motherboard are important. Memory speed can directly affect system performance. You should choose your memory modules by taking into account the maximum memory capacity and memory speed supported by your motherboard.
Expansion Slots:
- Your motherboard’s expansion slots are used to connect additional components (for example, video card, sound card, network card) to the motherboard. By determining which expansion slots you need, you should ensure that your motherboard has appropriate expandability options.
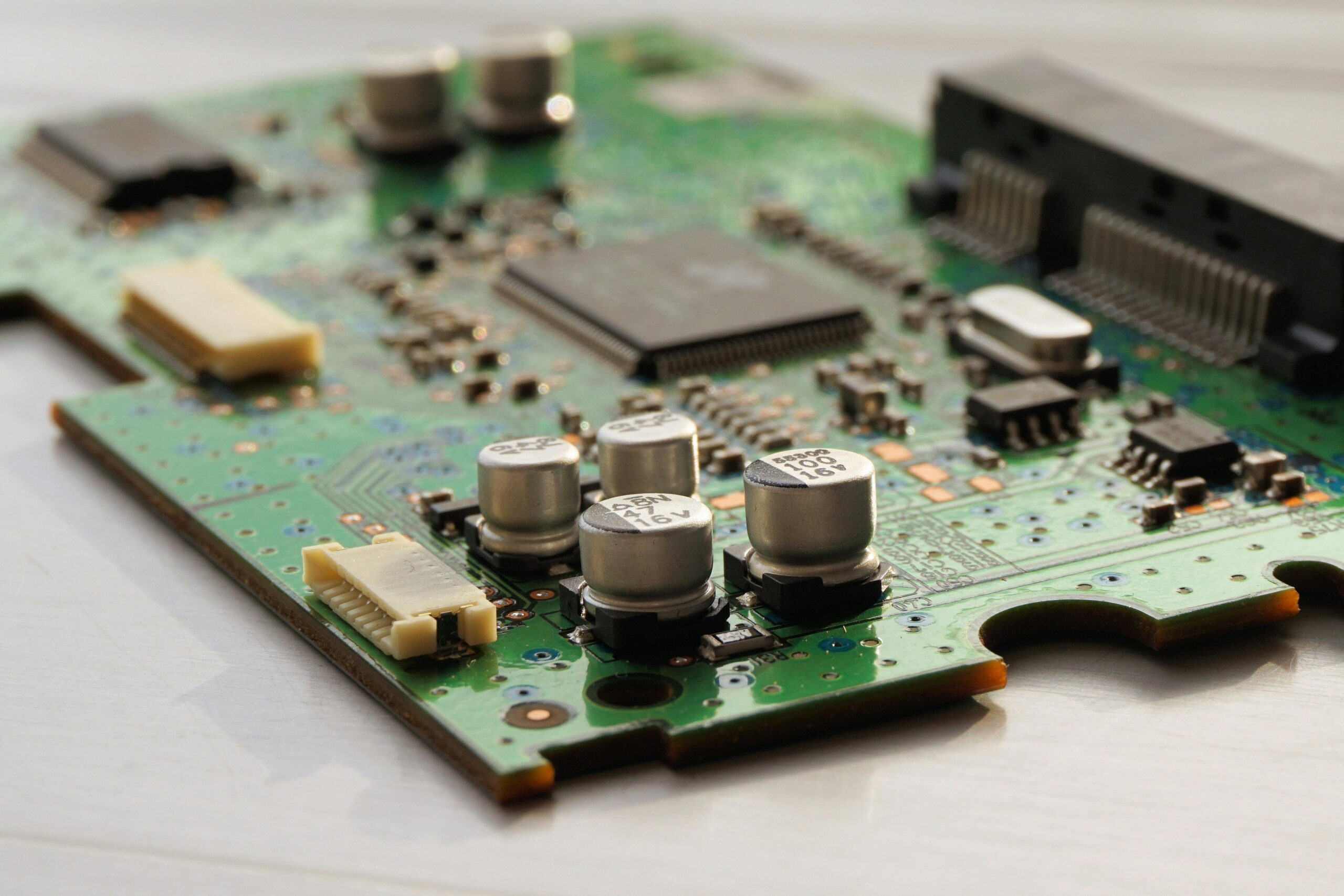
Storage Ports:
- Storage ports supported by your motherboard are used to connect storage devices such as hard disk drives, SSDs, and optical drives. By considering different storage connectivity options such as SATA ports and M.2 slots, you should choose a motherboard that will meet your storage needs.
Form Factor:
- The form factor of the motherboard must be compatible with the case. There are different form factors such as ATX, Micro ATX, Mini ITX and you should choose the motherboard according to the case. Additionally, the form factor determines the location and arrangement of components on the motherboard.
BIOS and Features:
- BIOS features and other additional features of the motherboard should also be taken into account. BIOS is the core system software of the motherboard and provides configuration of the hardware. Additionally, other features provided by the motherboard, such as USB ports, audio, and network connections, affect system performance and ease of use.
Processor Motherboard Compatibility
Compatibility between the processor and motherboard is determined by the socket type of the processor and the processor model supported by the motherboard. You should choose a compatible processor and motherboard by paying attention to the correct socket types.
Case Motherboard Compatibility
Case and motherboard compatibility depends on the internal dimensions of the case and the form factor of the motherboard. The case must match the form factor of the motherboard and have the necessary ports.
Why Does the Motherboard Burn?
Motherboards can burn out for a variety of reasons, including overheating, electrical problems, or component failures. This is usually related to components on the motherboard burning or overheating.
What are Motherboard Problems? How to Solve?
Motherboard problems can negatively affect the stability and performance of the computer. Here are common motherboard problems and how to fix them:
- Motherboard Not Powering Up or Failing to Startup: This issue can occur if the motherboard is unable to communicate with the power supply or there is an error during the startup process. To fix the problem, check the power supply, properly connect the power connections on the motherboard, and reset the motherboard’s BIOS.
- Ports on the Motherboard Not Working: If ports such as USB, audio or LAN are not working, this may indicate a problem with the motherboard. To solve this problem, first make sure that the drivers are up to date and the BIOS settings are configured correctly. Test the ports with different devices and replace the motherboard if necessary.
- Screen Problems: If the screen does not appear at all or shows abnormalities, it may be a sign of a problem with the motherboard. Check the video card, monitor and cable connections. Update the video card drivers and check the PCIe slot on the motherboard.
- Motherboard Temperature Issues: Motherboard overheating could be an issue with the cooling system or inadequate air circulation between components on the motherboard. Check the cooling elements on the motherboard and clean them if necessary. Add additional cooling solutions or adjust fan speeds.
- Motherboard BIOS Problems: Misconfigurations in the BIOS or an error during an update can prevent the motherboard from functioning properly. Reset BIOS settings to factory defaults and install an updated BIOS version if necessary.
- Hardware Incompatibilities: Hardware parts that are incompatible with the motherboard or conflict with each other can affect the stability of the system. To resolve this situation, select compatible hardware parts and replace components as necessary.
Motherboard problems are often caused by hardware or software incompatibility and can often be resolved when diagnosed correctly. However, it should be noted that in some cases, the motherboard may be physically damaged. In this case, the motherboard may need to be replaced.