What is “non-binary” memory?
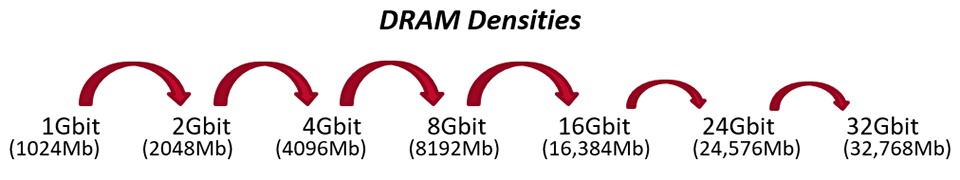
The density of DRAM chips increases periodically in order to meet the demand for memory capacity in computer systems.
Historically, the density doubles (e.g. from 4 Gbit to 8 Gbit, from 8 Gbit to 16 Gbit). But with DDR5, we have an intermediate density of 24 Gbit, also called “non-binary” memory.
The term “non-binary” comes from the divergence caused by the doubling of density. To increase density, DRAM semiconductor manufacturers must continually improve the design and process shrink the silicon wafer (measured in nanometers, or nm) in order to increase the number of memory cells, within the same package footprint (chip) than the previous generation.
This allows the same JEDEC printed circuit board (PCB) designs to be used for memory modules.
Why choose modules based on 24 Gbit (non-binary) rather than 16 Gbit?
In client computing, application requirements are evolving along with PC gaming and productivity.
It’s not uncommon to see the latest gaming titles recommend or require a minimum of 16 GB of RAM, with 32 GB being recommended for smoother gaming and multitasking.
In data center applications, such as those driving AI, the demand for higher capacities has also increased to process more data in memory.
24Gbit DRAM allows the use of 24, 48, and 96 GB registered DDR5 DIMMs, significantly increasing the capacity of multi-channel memory architectures and increasing capacity per core, without breaking the bank by investing in higher capacities using expensive 3DS stacked DRAM modules (128GB/256GB 3DS RDIMMs).
Which systems are compatible with modules based on 24 Gbit?
All DDR5 platforms from Intel and AMD are capable of supporting 24 Gbit memory. However, a BIOS update may be required before installing 24 Gbit based modules.
Platforms compatible with 24 Gbit
| System type | AMD | Intel |
|---|---|---|
| PC / Laptop | AMD Ryzen 4th Gen Chipset (AM5) / 600 series | Intel Core 14th Gen Chipset / 700 series
Intel Core 13th Gen chipset / 700 series Intel Core 12th Gen chipset / 600 series |
| Server / Workstation | AMD 4th Gen EPYC processors | Intel 4th Gen Xeon Scalable Processors
Intel Xeon W-3400/2400 processors |
Can we combine memory based on 24 Gbit with memory based on 16 Gbit?
For JEDEC compliant memory modules (ValueRAM, Server Premier, non-overclocking), it is possible to mix multiple banks, but we do not recommend mixing memory within the same bank group. On PCs/laptops, this disables channel architecture optimization, forcing the memory to operate at half its potential bandwidth. On servers, mixing within a multi-channel bank group is not allowed. If adding memory to the second bank group, it is always recommended to put the largest capacity memory in the first bank. Mixing memory modules or kits in a PC/laptop using overclockable memory